CamCyclopedia
CamCyclopedia(카메라 백과사전)에서 카메라에 대한 기본 원리와 갤럭시 카메라에 적용된 AI 기술과 주요 기능에 대해 알아보세요.
- Korea
- :
- 커뮤니티
- :
- CamCyclopedia
- :
- Understanding tones and tone enhancement for vibra...
Understanding tones and tone enhancement for vibrant photos
👨🎓Michael Brown (York University Professor)
※한글버전은 영어버전에 이어집니다.
Understanding tones and tone enhancement for vibrant photos
Samsung smartphone cameras make capturing photos convenient and easy. Users can now capture photos anywhere and at any time. This flexibility in image capture means we often take photos in places poorly suited for photography, such as dark or bright environments. Camera engineers work hard to develop algorithms that run in your camera hardware to ensure that you get high-quality, vibrant photos, even when capturing in non-ideal situations.
Figure 1. This figure shows an image captured using Galaxy S21 Ultra. The red, green, and blue color channels of this image are shown. We can convert the image to a luminance image to reveal the brightness at each pixel. An image histogram is a way of visualizing the tonal properties of the luminance image. The histogram represents the number of pixels in the image for each tonal value.
Tones and image histograms
One of the ways photos are improved is through tone enhancement. To understand tone enhancement, let’s first understand what an image tone is and how camera engineers visualize the tones in an image.
Images are represented as a two-dimensional grid of pixels, with each pixel composed of a red, green, and blue color. The combination of the red, green, and blue values produces the colors we see on our screens and in printed photos. Figure 1 shows an example of an image captured using Galaxy S21 Ultra. The image’s red, green, and blue channels are also shown. We can also convert our input image to a luminance image by selectively averaging the red, green, and blue values at each pixel. The luminance image allows us to understand the image’s tonal properties. In particular, a tone refers to the brightness level of each pixel, ranging from its darkest value to its brightest value. Images use a fixed number of tonal levels, typically 0 to 255 tones per image. We can visualize the tones in an image using a special plot called an image histogram. An image histogram is a visual representation that shows the number of pixels in the image with each tonal value. Figure 1 shows an example of the image histogram of the luminance image. The horizontal axis of the image histogram represents the tones from darkest (0) to brightest (255). The vertical axis shows the number of pixels in the image with each tonal value.
Figure 2. (Left) shows an underexposed (dark image) and its corresponding histogram. The histogram reveals that the image lacks tones in the bright region. (Right) shows an overexposed (bright image) and its corresponding histogram. The image has very few dark pixels. By examining these images’ histograms, we can determine whether the image quality can be improved. *Image simulated for illustrative purpose.
What does an image histogram tell us about image quality?
An image histogram reveals a lot about the quality of an image. For example, in non-ideal environments, our images often lack tones in dark or bright regions. For example, in Figure 2 (left), we see an underexposed image and its corresponding image histogram. The image was captured under a canopy of trees, resulting in a dark image. We can see in the image histogram that there are only a few bright tones. Even without seeing the actual image, we can predict this image will appear dark. Figure 2 (right) shows an overexposed image and its corresponding histogram. This image was captured in an environment with direct sunlight, resulting in a bright image. The histogram reveals that there are much fewer dark tones than bright tones. Again, even without seeing the captured image, we can predict this image will appear overly bright with few shadows and dark regions. Both of these images would likely not be preferred by the smartphone owner.
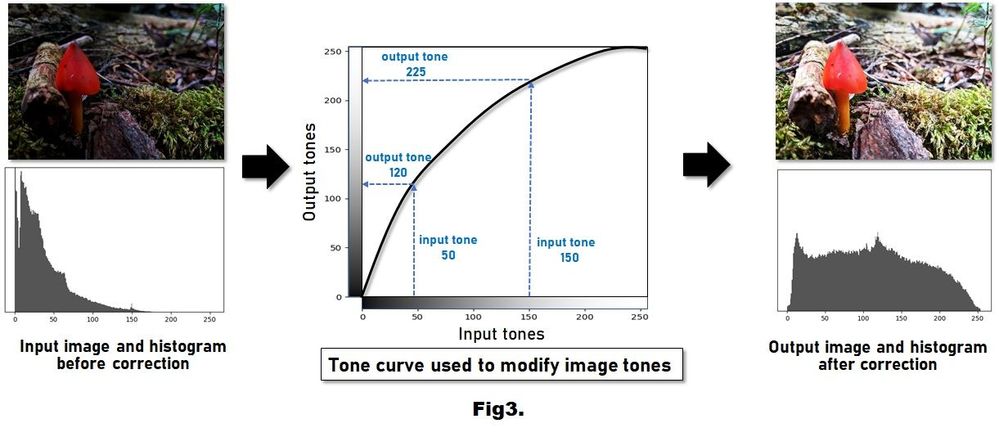
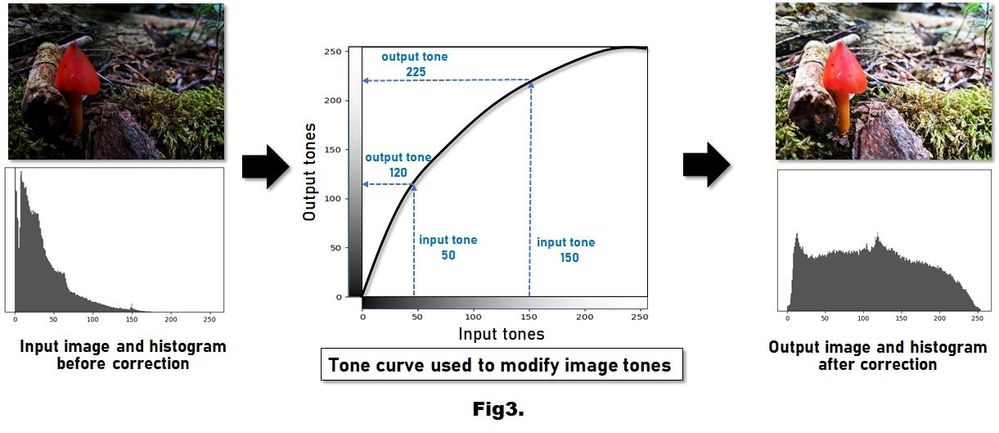
Figure 3. (Left) shows the underexposed image from Figure 2 and its histogram. (Middle) A tone curve enhances the image by adjusting its tonal values. This tone curve specifies how tones in the input image should be adjusted. This particular tone curve is increasing (or brightening) the tonal values. (Right) shows the resulting output image after tone manipulation. The image looks visually better. We also see that the corresponding histogram now spans the full tonal range. *Image simulated for illustrative purpose.
Making images better through tone enhancement
Your camera hardware can analyze the tonal properties of your image’s histogram and adjust the tones to enhance the image’s visual quality. An image’s tonal values are adjusted using a mechanism referred to as a tone curve. Figure 3 shows an example, where the underexposed image from Figure 2 is shown together with its histogram. This underexposed image will be the input to the image adjustment. In Figure 3 (middle), we see the tone curve as a 2D plot, where the horizontal axis of the plot represents the input tones, and the vertical axis represents the output tones. The tone curve specifies how to convert the tones in the input image to their new values in the output image. Based on the tone curve, we can see that all pixels in the input image with a tone value of 50 will have a tone value of 120 in the output image. The graph also shows that all input pixels with a tone value of 150 will be adjusted to have a tone value of 225 in the output image. The tone curve describes a tonal adjustment that increases (or brightens) the input tones in the image. The tone curve is typically designed to adjust the luminance image’s histogram. The tone curve is then applied to each red, green, and blue color channel of the input image to produce the output image. Figure 3 (right) shows the output image and its histogram after tone adjustment. Notice how the image looks more vivid. In addition, the histogram of the output image spans the full tonal range.
Figure 4. (Left) shows the overexposed image from Figure 2 and its histogram. (Middle) A tone curve enhances the image by decreasing (or darkening) the tonal values. (Right) shows the resulting output image after tone manipulation. The image looks visually better. We also see that the corresponding histogram now spans the full tonal range. *Image simulated for illustrative purpose.
Figure 4 shows another example of tonal adjustment using a tone curve, but this time applied to the overexposed image from Figure 2. In this example, the tone curve shown in Figure 4 (middle) has a different shape than the previous example because, for this image, we wish to darken the image. In particular, we can see that all pixels in the input image with a tone value of 100 will be adjusted to have a new tonal value of 30 in the output image. Pixels with an input tonal value of 200 will be adjusted to have a tonal value of 120 in the output image. This tone curve reduces (or darkens) the input tones in the image. Figure 4 (right) shows the resulting output image and its histogram after applying the tonal adjustment. The output image has much more detail and texture after the adjustment. As with the previous example, the histogram of the corrected image spans the full tonal range from 0 to 255.
Figure 5. (Left) shows an input image that spans most of the tonal ranges. (Middle) shows an S-curve, which simultaneously darkens and brightness tonal values in the image. This type of tone curve helps to increase the contrast and texture in the image. (Right) shows the output image and its histogram. * Image captured with Galaxy S21 Ultra.
Enhancing contrast through tone manipulation
The previous examples targeted images that lacked dark or bright tones due to under- and overexposure. Tone curve manipulation can enhance images even when the image already has a full tonal range. For example, Figure 5 shows an input image and its histogram. The image histogram spans most of the possible tones and does not look over- or underexposed. However, tone manipulation can still enhance the image’s visual quality. Figure 5 (middle) shows a tone curve commonly referred to as an S-curve because it resembles the letter S. To understand what the S-curve is doing to the tonal range, we first look at the middle tonal value of 128. This value does not change from the input to the output. However, all tone values below the middle tone are darkened. For example, an input tone of 50 will become 25 in the output. Conversely, all tones above the middle tone are brightened. For example, an input tone of 200 becomes 225 in the output. The S-curve adjusts the overall contrast by simultaneously darkening and brightening tones, producing a visually crisp and vibrant output image.
Summary
Tone enhancement can help fix problems related to over- and underexposure, as well as improve overall image contrast. Your Samsung smartphone is able to recognize different challenging lighting environments and compute the appropriate tone curves in real-time. The next time you share a vibrant photograph with your family and friends, think of the state-of-the-art technology on your smartphone, ensuring you get high-quality images night and day.
※ Tone enhancement availability and options may vary by phone model.
생생한 사진을 위한 톤 및 톤 개선 방법에 대한 이해
스마트폰의 발달에 따라 이제 사용자는 언제 어디서나 편리하고 쉽게 사진을 촬영할 수 있습니다. 이와 더불어 빛이 충분하지 않은 야간 상황과 같이 깨끗한 사진을 찍기 어려운 환경에서 스마트폰 카메라가 사용되는 빈도는 매우 증가했습니다. 따라서, 카메라 개발자는 사용자의 실사용 환경에 맞추어 어떠한 상황에서도 고품질의 생생한 사진을 얻을 수 있도록 다양한 영상 처리 알고리즘을 개발하기 위해 열심히 노력하고 있습니다.
그림1. 이 그림은 갤럭시 S21 Ultra로 캡처한 사진을 보여줍니다. 이는 빨강, 녹색 및 파랑 색상 채널로 표시할 수 있습니다. 세 가지 색상을 조합하면 각 픽셀의 밝기를 확인할 수 있는 휘도 영상으로 변환이 가능합니다. 마지막으로, 히스토그램은 영상의 톤 특성을 시각화하는 방법으로 각 휘도 값에 대한 영상 내 픽셀 수를 나타냅니다.
톤 및 히스토그램
사진을 개선하는 방법 중 하나는 톤을 보정하는 것입니다. 톤 보정을 이해하려면 먼저 영상의 톤이 무엇인지, 그리고 카메라 개발자가 영상의 톤을 어떻게 시각화하는지 이해해야 합니다. 일반적으로 영상은 이차원 픽셀 좌표로 구성되며, 각 픽셀은 빨강, 녹색 및 파랑 값의 조합으로 사진에서 볼 수 있는 색상을 표현합니다. 그림 1은 갤럭시 S21 Ultra로 촬영한 영상의 예를 보여줍니다. 영상은 빨강, 녹색 및 파랑의 세 가지 색상 채널로 분리할 수 있으며 또한 각 픽셀의 색상 정보를 조합하여 이를 휘도 영상으로 변환할 수 있습니다. 우리는 휘도 영상을 통해 영상의 톤 특성을 이해할 수 있는데, 일반적으로 톤은 각 픽셀의 가장 어두운 값 0부터 가장 밝은 값 255까지의 밝기 수준을 나타냅니다. 이러한 휘도 영상을 히스토그램으로 변환하면 영상의 톤을 시각화할 수 있습니다. 그림 1 오른쪽 마지막 영상은 히스토그램의 예를 보여주는데 가로축은 가장 어두운 값 0에서 가장 밝은 값 255까지의 톤을 나타내며 세로 축은 영상에서 각 톤이 가지는 픽셀의 개수를 나타냅니다.
그림 2. 왼쪽은 노출이 부족한 상태로 촬영된 영상과 그 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 왼쪽의 히스토그램은 영상의 밝은 영역에 톤이 부족함을 나타냅니다. 오른쪽은 노출이 과하게 찍힌 영상과 그 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 영상에 어두운 픽셀이 거의 없습니다. 이렇게 영상의 히스토그램을 보면 영상의 품질을 어떻게 개선해야 하는지를 알 수 있습니다. * 설명을 위해 시뮬레이션된 이미지입니다.
히스토그램을 통한 영상 화질 개선이란?
히스토그램을 통해 우리는 영상 품질을 어느 정도 확인할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 그림 2 왼쪽은 노출이 부족한 경우 촬영된 영상과 그 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 나무 그늘 아래에서 촬영했기 때문에 카메라에 들어오는 빛이 부족하여 어두운 영상이 생성되었습니다. 히스토그램을 보면 밝은 영역의 톤이 매우 적다는 것을 한눈에 알 수 있습니다. 즉, 실제 영상을 보지 않아도 히스토그램만 보면 어두운 영상인 것을 쉽게 예측할 수 있습니다. 이와 반대로 그림 2 오른쪽은 노출이 과다한 환경에서 촬영된 영상과 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 이 영상은 직사광선이 비치는 환경에서 촬영되었는데 히스토그램을 보면 밝은 톤보다 어두운 톤이 훨씬 적다는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 즉, 촬영된 영상을 보지 않아도 히스토그램 만으로 이 영상이 그림자와 같은 어두운 영역이 거의 없이 지나치게 밝게 나타날 것이라고 예상할 수 있습니다. 이러한 노출 부족 및 과다한 상태로 촬영된 두 영상은 사용자가 선호하지 않을 가능성이 높습니다.
그림 3. 왼쪽은 그림 2의 노출 부족 영상과 히스토그램입니다. 중앙 영상은 톤 매핑 곡선을 보여주는데 이를 조정하면 어두운 영상의 밝기를 개선할 수 있습니다. 오른쪽은 톤 보정 후 출력 영상 및 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 확실히 시각적인 표현력이 개선되어 보입니다. 해당 히스토그램을 보면 보정 전과 비교하여 전체 영역에 톤이 분포되어 있음을 쉽게 알 수 있습니다. * 설명을 위해 시뮬레이션된 이미지입니다.
톤 보정을 통한 영상 품질 개선
카메라 영상처리 하드웨어는 히스토그램의 톤을 분석하고 이를 보정하여 영상의 시각적인 품질을 향상시킵니다. 일반적으로 톤 매핑 곡선이라는 함수를 사용하여 영상의 톤을 보정합니다. 그림 3은 그림 2의 노출 부족 영상을 톤 보정으로 개선하는 방법에 대한 예시입니다. 그림 3 중간의 톤 매핑 곡선은 2차원 함수로 볼 수 있습니다. 여기서 함수의 가로축은 입력 톤을 나타내고 세로축은 출력 톤을 나타냅니다. 즉, 톤 매핑 함수는 입력 영상의 톤을 출력 영상의 새로운 톤으로 변환하는 방법을 의미합니다. 이 함수를 보면 톤 값이 50인 입력 영상의 모든 픽셀이 출력 영상에서 120의 톤 값으로 매핑됨을 알 수 있습니다. 또한 톤 값이 150인 모든 입력 픽셀이 출력 영상에서 225의 톤 값으로 보정 됨을 보여줍니다. 예시의 톤 곡선은 입력 영상의 톤을 증가 또는 밝게 하는 톤 보정 방법을 보여주며 이는 일반적으로 휘도 영상의 히스토그램을 조정하도록 설계되었습니다. 이러한 톤 커브는 입력 영상의 각 빨강, 녹색 및 파랑 색상 채널에 적용되어 최종 출력 영상이 생성됩니다. 그림 3 오른쪽은 톤 보정 후의 출력 영상과 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 보정 후 영상이 얼마나 더 생생하게 변했는지 확인해 봅시다. 주목할 점은 톤 보정 후 영상의 히스토그램은 보정 전 히스토그램과 달리 전체 영역에 걸쳐 톤이 존재하고 있다는 것입니다.
그림 4. 왼쪽은 그림 2의 노출 과다 영상과 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 중앙의 톤 곡선은 톤 값을 감소 또는 어둡게 하여 입력 영상을 향상시킵니다. 오른쪽은 톤 보정 후 출력 영상과 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 보정 후 영상이 시각적으로 더 좋아 보입니다. 또한 보정 후 영상의 히스토그램을 보면 톤이 전체 범위에 걸쳐 분포하고 있습니다. * 설명을 위해 시뮬레이션된 이미지입니다.
그림 4는 노출 부족이 아닌 노출 과다 영상의 품질을 톤 보정으로 개선하는 예시입니다. 여기서 그림 4의 중앙에 위치한 톤 커브를 보면 입력 영상을 어둡게 만들고 있습니다. 특히 톤 값이 100인 입력 영상의 모든 픽셀이 출력 영상에서 새로운 톤 값 30을 갖도록 보정되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 입력 톤 값이 200인 픽셀은 출력 영상에서 120이 되도록 조정됩니다. 이 톤 곡선은 영상의 입력 톤을 감소 또는 어둡게 만듭니다. 그림 4의 오른쪽은 톤 보정 후 출력 영상과 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 출력 영상은 톤 보정 후 훨씬 더 세밀하고 질감이 있게 보입니다. 앞의 예와 마찬가지로 톤 보정된 영상의 히스토그램은 0에서 255까지의 전체 범위에 걸쳐 톤이 적절하게 분포되어 있습니다.

그림 5. 왼쪽은 톤이 전체 범위에 고르게 걸쳐 있는 입력 영상과 히스토그램을 보여줍니다. 중앙의 톤 곡선은 어두운 톤은 더 어둡게 하고 밝은 톤은 더 밝게 보정하는 S 모양 톤 매핑 함수입니다. 이러한 유형의 톤 곡선은 영상의 대비와 질감을 높이는 데 도움이 됩니다. 오른쪽은 톤 보정 후 영상과 히스토그램입니다. * 이미지는 Galaxy S21 Ultra로 촬영되었습니다.
톤 보정을 통한 대비 개선
이전 예제에서는 노출 부족 및 노출 과다로 인해 어둡거나 밝은 톤이 부족한 영상을 어떻게 개선하는지 보았습니다. 하지만 적절한 노출로 이미 전체 영역에 톤이 분포하는 경우에도 톤 보정을 통해 영상 품질을 개선할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 그림 5의 입력 영상의 히스토그램은 가능한 대부분의 톤에 걸쳐 있으며 노출 과다 또는 부족으로 보이지 않습니다. 그러나 톤 보정은 여전히 영상의 시각적 품질을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 그림 5의 중앙은 문자 S와 유사하기 때문에 일반적으로 S-곡선이라고 하는 톤 매핑 함수를 보여줍니다. S-곡선이 톤 범위에 대해 수행하는 작업을 이해하기 위해 먼저 중간 톤 값 128을 살펴봅니다. 이 값은 입력과 출력이 동일합니다. 그러나 중간 톤 아래의 모든 톤 값은 어두워집니다. 예를 들어, 50의 입력 톤은 출력에서 25가 됩니다. 반대로 중간 톤 위의 모든 톤은 밝아집니다. 예를 들어, 200의 입력 톤은 출력에서 225가 됩니다. S-곡선은 어두운 톤은 어둡게 하고 밝은 톤은 밝게 함으로써 전체 대비를 조정하여 시각적으로 선명하고 생생한 출력 영상을 생성합니다.
요약
톤 보정은 노출 과다 및 노출 부족과 관련된 문제를 해결하고 전반적인 영상의 대비를 개선하는 데 도움을 줄 수 있습니다. 삼성 스마트폰은 다양한 까다로운 조명 환경을 인식하고 실시간으로 적절한 톤 곡선을 계산합니다. 톤 개선 기술이 적용된 삼성 카메라를 사용해 밤낮으로 고품질의 생생한 사진을 가족 및 친구들과 공유하고 즐겨주세요.
※ 톤 개선 가능 여부 및 옵션은 휴대폰 모델에 따라 다를 수 있습니다.
CamCyclopedia(카메라 백과사전) 목차 바로 가기
CamCyclopedia 소개글 바로 가기
이외에도 CamCyclopedia는 커뮤니티 -> 카테고리(app) -> CamCyclopedia -> “CamCyclopedia 목차”를 통해 언제든지 확인하실 수 있습니다.
여기에 의견을 추가하려면 등록된 사용자이어야 합니다. 이미 등록되어 있다면 로그인하시기 바랍니다. 아직 등록하지 않은 경우 등록 후 로그인하시기 바랍니다.