- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-26-2020 12:14 PM in
Galaxy SResearch by: Ohad Mana, Israel Wernik, Bogdan Melnykov, Aviran Hazum
Intro
Check Point researchers have recently discovered a new clicker malware family, along with fresh samples of the Joker malware family in Google Play.
Throughout this publication we present a brief overview of the malicious campaigns, and describe the technical analysis that has been performed around the two families of malware.
Analysis
‘Haken’ & ‘BearClod’ Clickers:
- Overview:
Clickers, malware that mimics the user and perform ‘clicks’ on ads, are a rising threat in the mobile industry. Recently, UpsteamSystems published a report regarding a clicker dubbed ‘ai.type’ or ‘BearClod’. We have observed an increase in activity and scale of the operation behind this clicker, with 47 new applications that were available on Google Play, and were downloaded more than 78 million times by users.
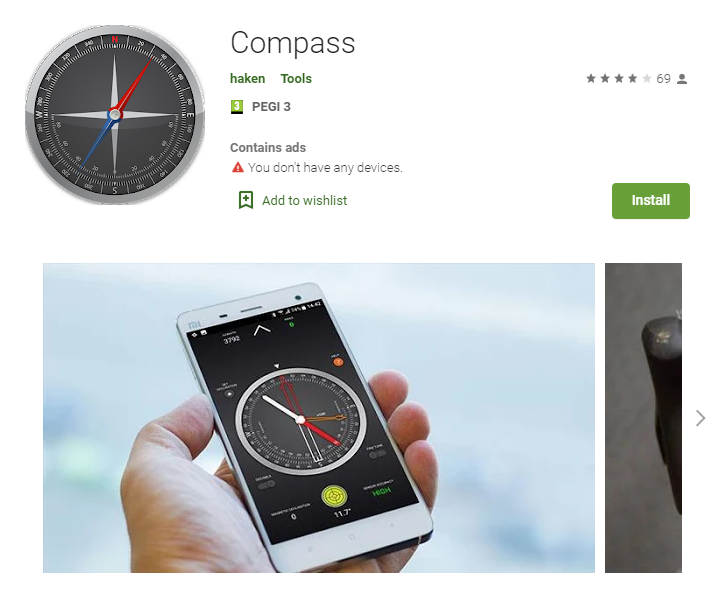
While monitoring the increased activity of ‘BearClod’, we were able to find another clicker family: ‘Haken’. This campaign has just begun its path in Google Play. With 8 malicious applications, and over 50,000 downloads, the clicker aims to get a hold of as many devices as possible to generate illegitimate profit.
Figure 1 – Haken Clicker Application on Google Play
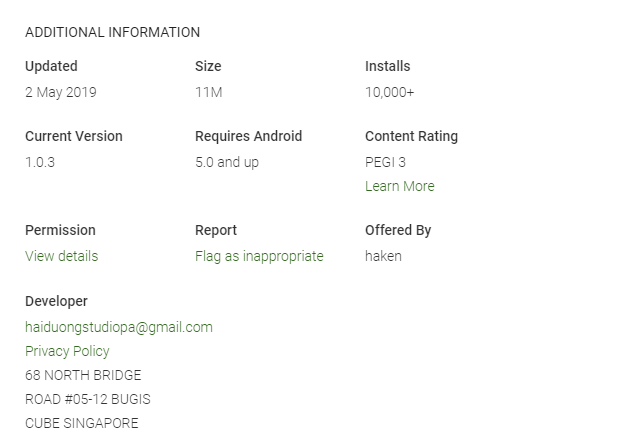
Figure 2 – Haken Clicker Details from Google Play
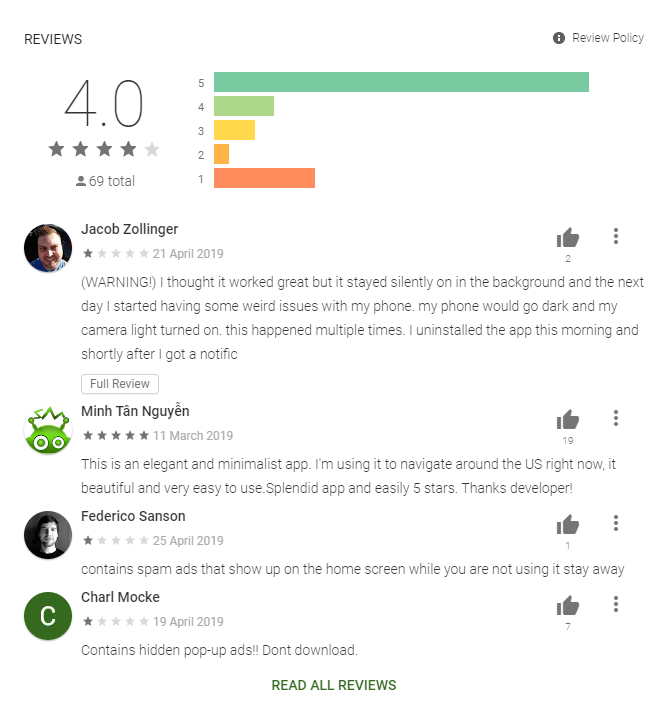
Figure 3 – Google Play reviews and comments for Haken Clicker
- Capabilities:
Both ‘BearCloud’ and ‘Haken’ clicker families use different approaches for the implementation of the clicking functionality. While the ‘BearClod’ utilizes a web-view creation and loading of malicious JavaScript code that performs the clicking, the Haken clicker utilizes native code and injection to Facebook and AdMob libraries while communicating with a remote server to get the configuration.
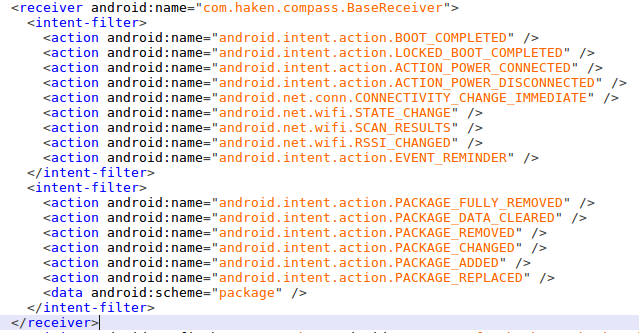
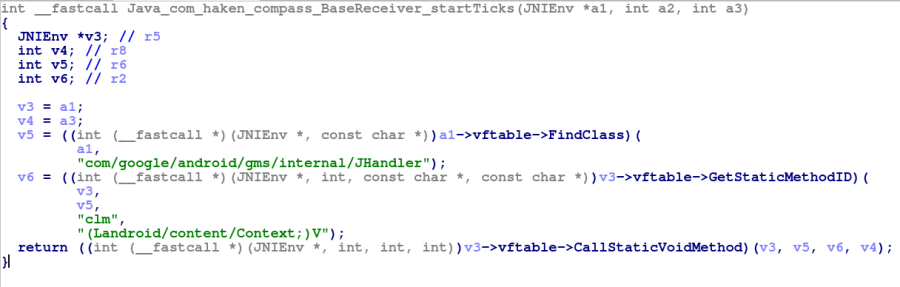
The first entry point of the Haken clicker is the receiver called ‘BaseReceiver’. This receiver asks for permissions that the backdoored app (in this case, a compass application that actually provides a compass service) does not require to function, for instance,BOOT_COMPLETED which let the backdoored application to run code at device start-up.
Figure 4 – Haken Clicker Permissions
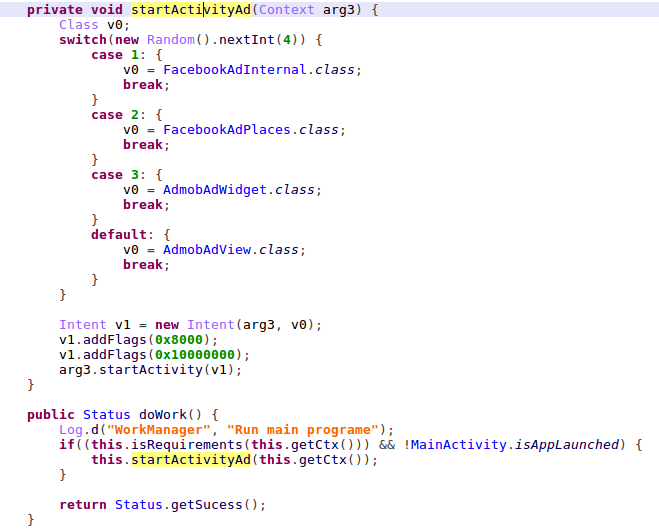
This BaseReceiver loads a native library ‘kagu-lib’ and calls from it a method called ‘startTicks’, which after inspection calls the method ‘clm’ from ‘com/google/android/gms/internal/JHandler’. This class registers two workers and a timer. One worker communicates with the C&C server to download a new configuration and process it, while the other is triggered by the timer, checks for requirements and injects code into the Ad-related Activity classes of well-known Ad-SDK’s like Google’s AdMob and Facebook.
Figure 5 – startTicks function
Figure 6 – Communication with C&C to get configuration
Figure 7 – Processing the configuration
Figure 8 – Injection into Facebook and Google
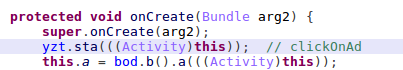
The clicking functionality is implemented in the code that was injected into the Ad-SDK’s ‘onCreate’ function, in this case, it’s the ‘yzt.sta’ method.
Figure 9 – Calling the injected code
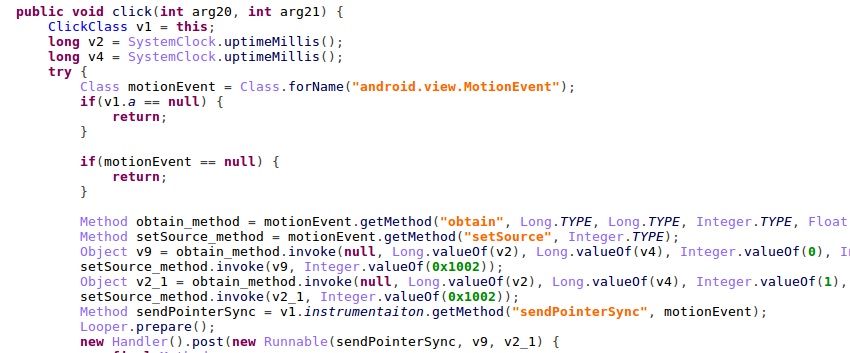
While using ‘MotionEvent’ to mimic user clicks, those functions are called via reflection.
Figure 10 – Clicking on ads received from the Ad-SDK via reflection on MotionEvent’s obtain.
After reporting this threat to Google, all of the affected applications were removed from Google Play, and most of them have already published a new version without the threat.
Continuing to read : https://research.checkpoint.com/2020/android-app-fraud-haken-clicker-and-joker-premium-dialer/- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-26-2020 06:17 PM in
Galaxy S- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-20-2025 10:13 PM in
Galaxy S- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-20-2025 10:13 PM in
Galaxy S